An ammeter is a device that is used to measure the flow of electric current in a circuit.
When an ammeter is connected in series with a circuit, it becomes a part of the circuit and experiences the full current flowing through it.
High current may damage the instrument and here comes the role of Swamping Resistance. Let’s see.
You can watch the quick video below or read along
Need for swamping resistance in an instrument when it is used as an ammeter
Firstly let us know what is meant by swamping resistance.
Swamping resistance:- Swamping resistance is a resistance that is connected in series to a galvanometer, resulting in equivalent coil resistance as Rsw + Rm. It is used to reduce the temperature effect.
Now, Let us understand the reason of connecting swamping resistance in an instrument when it is used as an ammeter with the help of circuit diagram.
Consider the circuit below. The network consists of an ammeter, a battery, a load .
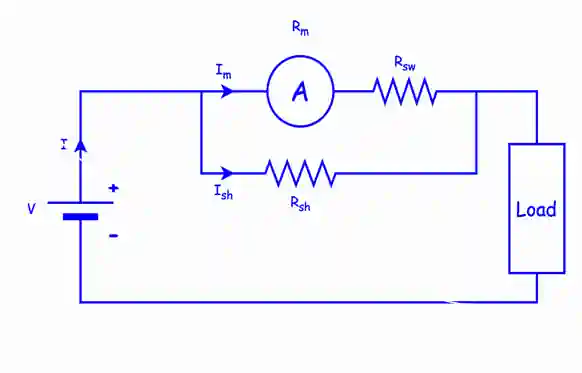
WE will consider the case PMMC instrument is used as an ammeter. We can use PMMC instruments as both ammeters as well as voltmeter.
We know that the ammeter is used for measuring current.
When we are using PMMC instrument as an ammeter, the range of that ammeter is very very small. i.e. it can measure current up to 5 μA . It the current more than 5 μA then the instrument will get damaged.
In the network, we can see that resistance is connected in parallel to the ammeter, this resistance is called as the shunt resistance. This shunt resistance is used to bypass the extra amount of current.
In simple terms, we can say that the 5 μA current will flow through the ammeter because its range is 5 μA but the remaining 1 A current is bypassed by the shunt resistance. The load requirement of 6 μA is now is fulfilled. The use of a shunt resistor has prevented the instrument from damage.
Therefore, if we are using a PMMC instrument as an ammeter, we can increase the range of the ammeter by connecting the shunt resistor .
Due to this arrangement, the temperature rise will take place which will change the resistance as temperature and resistance is directly related to each other and that will cause an error in the reading of the ammeter. To minimize the temperature variation we are connecting a resistance in series with ammeter called as swamping resistance.
By connecting swamping resistance, errors can be minimized. The temperature effect will also get minimized. Here, the shunt resistance and swamping resistance both are made up of same material i.e. manganin. The value of shunt resistance is very small and the value of swamping resistance is very very large i.e. 10 to 20 times greater than the meter resistance.
We see that, the dominant resistance is the swamping resistance.
Characteristics of swamping resistance
Minimization of error :- The most desirable characteristic of the swamping resistance is that the error is minimized. As it is connected in series with the ammeter the temperature effect is minimized and therefore, the error also gets minimized.
Zero temperature coefficient ( no effect of temperature change) :- One of the most important characteristics of swamping resistance is that there is no effect of temperature change. As it is made up of manganin, it has a low-temperature coefficient. We know that temperature and resistance both are related to each other. As temperature increases, resistance also increases. Similarly, if temperature decreases, resistance also decreases. We can say that the resistance and temperature are directly related.
So, The swamping resistance is used to minimise the error. The swamping resistance is used to compensate the error due to temperature variations.
This is the reason of using swamping resistance in a PMMC instrument as an ammeter.
Hope, this article has cleared the concept that why there is need for swamping resistance in an instrument when it is used as an ammeter
Simple !!
Do not forget to check our Awesome GATE courses.


