In the world of electrical engineering, the network theorems plays a very crucial role. In order to solve the various circuit problems, need of network theorems is very essential.
In this article, you will understand the need for thevenin’s equivalent circuit with the help of real life examples and learn Thevenin’s theorem in detail.
Thevenin’s Theorem
Thevenin’s Theorem states that ‘ Any linear circuit containing several voltages and resistances can be replaced by just one single voltage in series with a single resistance connected across the load“
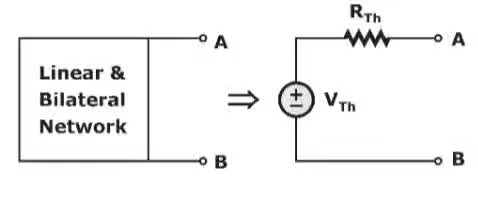
Need for converting a circuit into an Equivalent circuit
While solving problems based on Thevenin’s Theorem we see that we have to first convert the circuit into single voltage source and a series resistor.
But Have you ever imagined What is the need of converting the big circuit into an equivalent circuit?
Here is the reason for that, First and foremost, converting a circuit into its Thevenin’s equivalent allows us to simplify complex circuits into a simpler and more manageable form.
By reducing the original circuit to a single voltage source and a series resistor, we can analyze and understand the behavior of the circuit with greater ease. This simplification saves time and effort, especially when dealing with large and intricate circuits.
Thevenin’s equivalent circuit facilitates circuit analysis and calculations. It provides a practical way to determine the voltage, current, and power relationships within a circuit.
By replacing the original circuit with an equivalent circuit, we can apply basic circuit analysis techniques, such as Ohm’s Law and Kirchhoff’s Laws, to solve for desired parameters.
This simplifies the mathematical computations and enables efficient analysis of circuit performance.
Applications of Thevenin’s Theorem
Thevenin’s equivalent circuit also plays a crucial role in circuit design and troubleshooting. It helps us predict how a circuit will behave under different conditions and loads.
By using the equivalent circuit, we can assess the circuit’s response to varying load resistances and understand its stability and performance characteristics. This information is vital for designing robust and efficient electronic systems.
Here are some of them :-
i) Circuit Simplification :- Thevenin’s theorem allows complex circuits to be reduced to simpler equivalent circuits, which are easier to analyze. By finding the Thevenin equivalent circuit, you can determine the behavior of the original circuit with a reduced number of elements.
ii) Load analysis :- Thevenin’s theorem is often used to analyze how a circuit will respond to different loads. By finding the Thevenin equivalent circuit, you can easily calculate the voltage, current, and power delivered to a load connected to the circuit.
iii) Maximum Power Transfer :- Thevenin’s theorem is used to determine the load resistance that maximizes power transfer from a circuit to the load.
iv) Network analysis :- Thevenin’s theorem can be applied in network analysis to study the behavior of interconnected systems.
Now summarizing it all, we can say that In Thevenin’s Theorem, the equivalent circuit is formed by connecting the resistance in series with the voltage source.
Similarly in Norton’s theorem, The current source is connected in parallel with the resistance. In Norton’s theorem, also we need to convert the circuit into equivalent form.
Hope, so! This article had cleared many of your doubts as to why there is a need to convert the circuit into equivalent form.
Best Course for Networks
By Dr. Shilpa Sambhi